The product management lifecycle is the journey that guides a product from concept through launch, ensuring it meets user needs and business goals. Navigating this process can be complex, with numerous tasks and stakeholders involved. User story mapping offers a powerful way to simplify each phase, keeping teams aligned and focused on the user’s journey.
By visually organizing tasks around user experiences, story mapping enhances collaboration, supports prioritization, and makes it easier to communicate progress. In this article, we’ll explore how story mapping can add value across key stages of the product management lifecycle—from discovery and MVP slicing to prioritization, backlog management, and stakeholder engagement—helping teams deliver more user-centered, impactful products.
1. Product Discovery/Kickoff: Building a User-Centric Foundation
The discovery or kickoff stage sets the foundation for the entire product. At this point, it’s crucial to align the team on user needs, establish clear objectives, and ensure everyone understands the problem being solved. A user-centric approach is critical, as it helps keep the focus on delivering genuine value rather than just features.
Story mapping is particularly valuable during discovery because it guides teams to build the product around the user journey. By mapping out each step the user will take, teams can gain insight into how users interact with the product, what they want to achieve, and where their pain points lie. This process provides a structured way to capture the “big picture” and highlight areas needing more attention or further definition.
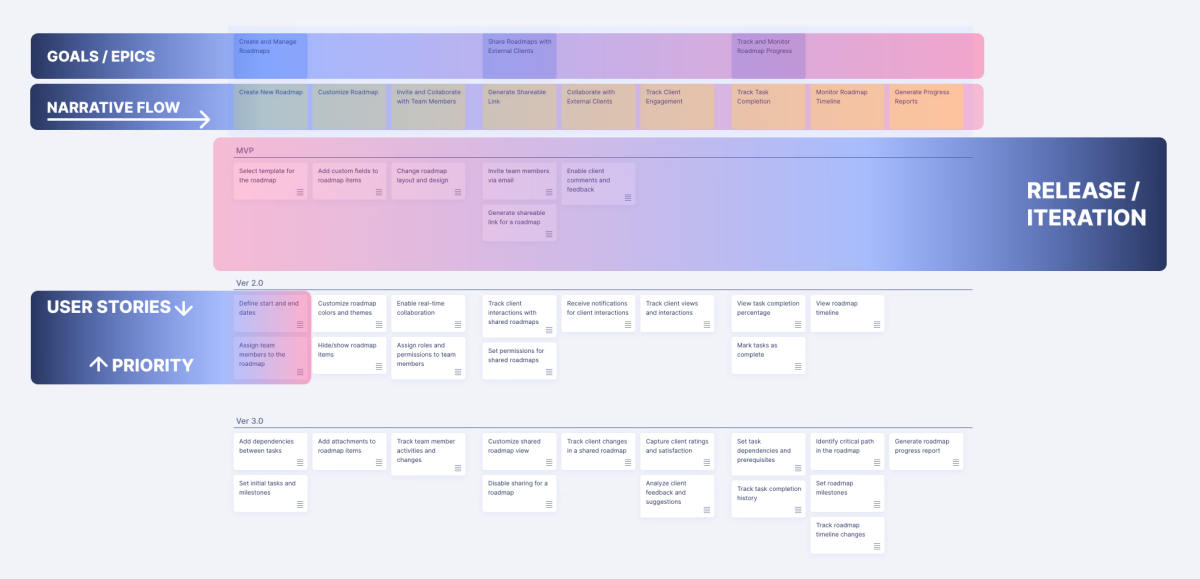
In practical terms, a story map acts as a shared visual blueprint for the product, which teams can use to spot gaps and spark conversations. For instance, mapping user goals early on can reveal crucial features or functions that might otherwise go overlooked. It also allows cross-functional teams—designers, developers, marketers, and stakeholders—to contribute their perspectives in the context of the user’s journey, leading to a richer, more balanced view of the product.
2. Slicing the MVP: Prioritizing for Impactful First Releases
The Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is the first version that offers enough functionality to meet core user needs. Slicing out the MVP is critical, allowing teams to deliver value quickly without overloading the initial release. Prioritizing what’s essential and deferring non-critical features helps teams avoid scope creep, optimize resources, and gather early feedback from real users.
Story mapping is ideal for defining an MVP because it visualizes the product’s core user journey and separates essential functions from nice-to-have features. By organizing user stories horizontally, teams can easily see which actions are critical for the user to achieve their primary goals. This structure naturally reveals which features should be included in the MVP and which can be saved for future iterations.
With a story map, teams can “slice” vertically across the map to define a narrow yet complete user journey for the MVP. This ensures the first release has all the components needed for users to achieve their primary objectives. This approach keeps the team focused on delivering a coherent experience rather than scattering efforts across less critical features. Story mapping also makes dependencies and task relationships visible, which helps avoid bottlenecks and allows for more efficient planning.
Ultimately, story mapping supports a streamlined, user-centered approach to MVP development. Providing a clear view of what’s essential enables teams to build a product that delivers immediate value to users while setting the stage for future enhancements based on real-world feedback.
3. Prioritization: Streamlining Decisions with a Visual Layout
Effective prioritization is crucial for product development, as it ensures that the team focuses on high-impact features that align with user needs and business goals. With limited time and resources, teams must make strategic choices about what to build first, often balancing immediate value with long-term objectives. Clear prioritization helps prevent wasted effort and keeps everyone aligned on the most critical tasks.
Story maps make prioritization intuitive by providing a clear, vertical layout that ranks features by importance. As tasks are organized from top to bottom based on priority, it becomes immediately visible which features or steps are essential to the product’s core experience and which can be scheduled for later. This layout not only simplifies decision-making but also encourages a collaborative approach to prioritization, allowing stakeholders to see, at a glance, what matters most and why.
Story mapping enables teams to discuss and adjust priorities collaboratively, ensuring that every decision reflects a shared understanding of the product’s goals. For instance, during planning sessions, teams can shift tasks up or down to respond to new information, changing priorities, or resource constraints. This flexibility ensures the roadmap remains aligned with the user journey and the overall business strategy.
4. Backlog Management: Staying on Track with a Clear Overview
As a product evolves, the backlog can quickly become overwhelming, filled with feature requests, improvements, and bug fixes. Effective backlog management is essential to keep the team focused on meaningful progress, prioritizing the most valuable tasks without losing sight of longer-term goals. A well-managed backlog provides clarity, structure, and adaptability, helping the team stay on track despite shifting priorities.
Story mapping brings clarity to backlog management by offering a high-level, visual representation of tasks within the broader context of the user journey. Rather than a long, fragmented list of items, a story map organizes the backlog into logical, user-centered steps. This structure makes it easy to see the relationship between tasks, track progress, and ensure alignment with the product’s overall vision.
With a story map, teams can regularly review and update the backlog to align with the user journey, moving tasks up, down, or across based on shifting priorities or new insights. This flexibility allows the team to respond to user feedback, market changes, or resource availability without losing focus on the big picture. Additionally, because a story map provides a shared visual tool, it facilitates more effective discussions around backlog refinement, ensuring that everyone—from developers to stakeholders—understands what’s prioritized and why.
5. Stakeholder Engagement and Buy-In: Building Trust Through Transparency
Engaging stakeholders and securing their buy-in is essential for a successful product. To feel confident in its potential, stakeholders—executives and department heads to external partners—need a clear understanding of the product’s direction and progress. Transparent communication helps ensure continued support, resource allocation, and goal alignment, especially when adjustments or pivots are necessary.
Story mapping is a powerful communication tool, making the product journey easy to understand, even for those who may not be deeply involved in day-to-day development. With its intuitive layout, a story map visually organizes features and tasks around the user journey, allowing stakeholders to see how the product will deliver value. This transparency fosters trust, as stakeholders can quickly grasp the product’s objectives, current status, and future priorities.
Involving stakeholders in story mapping sessions also encourages a collaborative approach, giving them a direct role in shaping the product. For example, during mapping sessions, stakeholders can offer insights based on their expertise, helping refine priorities, align on key outcomes, and address potential concerns early on. This collaboration enhances the product’s quality and builds stronger support, as stakeholders feel their perspectives are considered and valued.
Additionally, the story map’s structure helps stakeholders understand prioritization decisions by visually demonstrating the importance and order of features. When stakeholders see how tasks are prioritized in alignment with user goals, they’re more likely to support strategic choices and any necessary trade-offs. This shared understanding helps reduce resistance to changes and increases flexibility in navigating shifts in scope or direction.
Continuous Discovery: Close the Loop with Metrics and Experiments
Continuous discovery and experiment-driven development sit at the core of modern product practice. Treat your story map as a living hypothesis board: each slice is an assumption about user value that you should validate with real signals, not opinions. This tight loop cuts time-to-learning and aligns product, design, engineering, marketing, and growth around measurable outcomes.
Layer outcomes and growth signals right on the map—activation, adoption, retention, and monetization. Instrument key steps with analytics events, plan lean experiments for each slice, and route qualitative feedback (research notes, support tickets, reviews, in-product surveys) back to the relevant stories. Over time, the map turns into a single source of truth for what you tested, what worked, and why.
- State a clear hypothesis and expected impact (OKR/North Star) for each epic or story.
- Add a measurement plan—analytics events, target thresholds, and the dashboard that proves success.
- Design a lean test per slice (prototype test, fake door, A/B, or landing-page smoke test) and set a decision rule.
- Close the loop by attaching results to the story and marking keep/iterate/kill decisions.
- Continuously feed insights into prioritization and backlog refinement so validated ideas move up and weak bets fall away.
Summary
User story mapping is a versatile and powerful tool that enhances the product management lifecycle across each stage, from concept to launch. Story mapping ensures teams stay aligned on user needs and business goals by visually organizing features and tasks around the user journey. During product discovery, it establishes a user-centered foundation, guiding the team to focus on meaningful features. Story mapping helps isolate core functionalities for MVP slicing, ensuring an impactful first release that delivers value. In prioritization, the visual layout simplifies decision-making, helping teams focus on high-impact features first. Story mapping provides clarity regarding backlog management, keeping teams organized and adaptable even as the product evolves.
Moreover, stakeholder engagement benefits from story mapping’s transparency, enabling a clear understanding of the product journey and fostering stronger support and buy-in. By integrating story mapping into each stage of the product management lifecycle, teams can create more cohesive, user-centered, and impactful products while ensuring all stakeholders are aligned and engaged in the product’s success.
FAQ: User Story Mapping Across the Product Management Lifecycle
What is user story mapping?
It’s a visual way to organize work around the user journey—goals, activities, and tasks in context. Making the flow explicit aligns the team on user value and the big picture.
When should we create a story map?
Start in discovery or kickoff to build a shared understanding of the problem and users. Keep it alive through MVP slicing, prioritization, backlog refinement, and stakeholder reviews.
Who should be involved?
Include product managers/owners, business analysts, designers, engineers, QA, marketing, and key stakeholders. A cross-functional group brings diverse insight and speeds alignment.
How does story mapping help define an MVP?
It makes the end-to-end journey visible and separates essentials from nice-to-haves. Teams slice vertically to ship a coherent first experience and surface dependencies early.
How does it improve prioritization?
The vertical layout makes importance visible and ties priorities to user outcomes and business goals. It enables collaborative trade-offs and quick course corrections as new insights emerge.
How often should we update the map?
Review it regularly during refinement, after user feedback, and when priorities shift. Frequent updates keep the backlog, releases, and roadmap anchored to real user needs.
What’s the difference between a story map and a backlog?
A story map shows how work fits into the user journey. The backlog is a sequenced list; the map informs its order and releases.
How does story mapping support stakeholder buy-in?
It makes the product journey clear—even for non-technical audiences. Bringing stakeholders into mapping sessions builds trust, aligns expectations, and lowers resistance to trade-offs.
What pitfalls should we avoid?
Don’t over-detail too early or map features without tying them to user goals. Don’t let the map go stale—validate with users and update as you learn.
How do we measure success with story mapping?
Look for clearer MVP definitions, faster prioritization decisions, fewer scope tangles, and stronger stakeholder alignment. Track qualitative feedback plus delivery metrics like cycle time and release outcomes.
